Exfat Support Mac

ExFat is the only option I know which is natively supported by both Windows and Mac. If there's a 3rd option and which is supported by Netgear, happy to know. Model: R6300v2 AC1750 Dual Band Gigabit router.
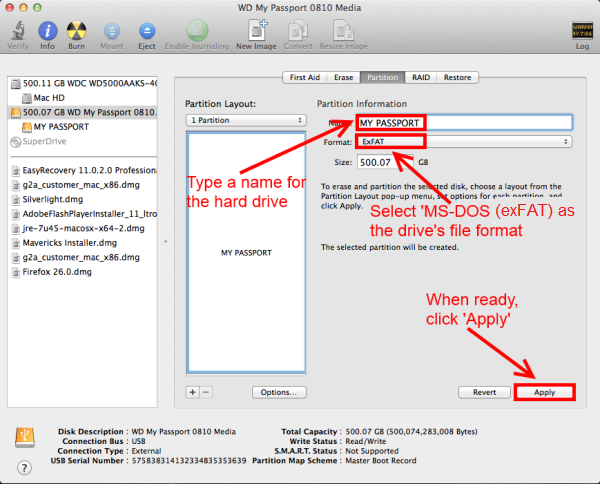
- Any Mac running 10.6.5 (Snow Leopard) or 10.7 (Lion) supports exFAT, while PCs running Windows XP SP3, Windows Vista SP1, and Windows 7 are compatible. If you know you’ll be using computers running updated versions of these operating systems, exFAT is the clear best choice.
- Fortunately for Mac users, Apple has an agreement with Microsoft and so OS X supports exFAT drives (as of Snow Leopard). You can plug in an external exFAT USB drive and read and write to it on your Mac. You can take an existing disk and reformat it as exFAT right from OSX.
- I can confirm that after I re-formated my external 2 TB HDD from exFAT with 2048K allocation unit size to exFAT with 1024K allocation unit size, the disk is now discoverable by Mac OS and I can work with it just fine. – retif Jul 14 '19 at 14:22.
Summary :
Which allocation unit size should you use for an exFAT partition? What is the best allocation unit size for exFAT format? If you are confused about the allocation unit size exFAT, don't worry. This post from MiniTool will show you how to set the right allocation unit size for exFAT partition.

Quick Navigation :
Exfat Support Mac
When you try to create or format a drive to exFAT with disk management tools, you are able to choose a proper allocation unit size for the exFAT partition according to your needs. However, not many users have a clear understanding about what allocation unit size is and what allocation unit size they should use for exFAT format.
Here is the full guide of NTFS vs FAT32 vs exFAT. Check out this post to know the differences.
Given that, this post will demonstrate you what allocation unit size is and how to set the best allocation unit size for exFAT format. If you are interested in this, please keep on reading.
About Allocation Unit Size
In computer file systems, a cluster or allocation unit refers to the smallest logical amount of disk space that can be allocated to hold a file. We know that hard drives are divided into many clusters to save data on it, but how big is a cluster? Well, the size of a single cluster is decided by the allocation unit size selected when the partition is created or formatted.
So, allocation unit size is also known as cluster size, which determines the smallest chunk of disk space that holds a file.
What is allocation unit size? What is another name for a file allocation unit? How can you change allocation unit size? You will get the answers in this post.
When you create or format a partition, you can set the allocation unit size for the partition. And usually, the allocation unit size will be set as Default, as many people don't know what it is and how to set it. So they just use the default value for the allocation unit size. And some users don't even notice the allocation unit size option.
Actually, the allocation unit size or cluster size can influence your disk performance or disk space utilization. If the allocation unit size is not set properly, it may reduce the data read-write speed and waste a lot of disk space.
So it is very necessary to change cluster size reasonably. And before changing cluster size for your partition, you can check out the following contents to learn what the best allocation unit size is or what allocation unit size should you use for exFAT.
What Allocation Unit Size Should I Use for exFAT?
As mentioned before, cluster size represents the smallest amount of disk space that can be used to hold a file.
One cluster can only hold one file, but one file may take up multiple clusters depending on the file size and the cluster size. This is to say, if the file's actual size is smaller than the size of a cluster, it will still take up a cluster. If the file's actual size is more than a cluster, the file will take up two or more clusters.
Therefore, if you save large files to a drive that uses small clusters, data read-write speed will be reduced, because each file is broken into small pieces and it needs time to gather all the broken pieces and access them as one. If you save small files to file system with large clusters, a lot of disk space will be wasted. And that’s why you should set cluster size reasonably.
So we get this conclusion: if the size of the files you want to store on the drive is large, then a large cluster size is recommended, which will increase the data read-write speed. How to clean your mac from viruses. If you plan to store lots of small files, it is advisable to set a small cluster size, which can improve the disk space utilization.
Exfat Support Mac Computers
If you have no idea about your file size and unit, Default is also a good choice. It will choose a proper cluster size for your drive based on the capacity. For example, according to Microsoft, the executing standard of default cluster size for exFAT is:
- 7MB – 256MB: 4KB
- 256MB – 32GB: 32KB
- 32GB – 256TB: 128KB
- >256TB: Not supported
Which allocation unit size you should use for exFAT format? Now you should know that it depends on the size of the file you will store on the exFAT drive. Besides, if you want to learn more information about the default cluster sizes for other file systems, you can check out this post from Microsoft: Default cluster size for NTFS, FAT, and exFAT.
How to Change Allocation Unit Size for exFAT
Now you should it is necessary to choose a proper allocation unit size for your exFAT, NTFS to FAT32 partition. If you want to change cluster size to improve your disk performance or enhance the disk space utilization, you can try the following two methods to change allocation unit size for exFAT partition.
Change Allocation Unit Size exFATwith MiniTool Partition Wizard
MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition is an all-in-one partition manager, which can help you manage NTFS, FAT32 and exFAT partitions in a simple way.
As a powerful partition manager for Windows users, it can help to move/resize partition, format partition, extend partition, copy disk/partition, convert NTFS to FAT32, convert MBR to GPT and check file system and so on.
With the Format Partition feature in MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition, you can clear all the partition data and then reconfigure parameters such as partition label, file system and cluster size for the specified partition. So, by formatting the drive, you can reset the allocation unit size exFAT so as to meet your actual demands.
Here are detailed steps:
Step 1.Download MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition by clicking the following button. Then install and launch MiniTool Partition Wizard to get its main interface.
Exfat Support Mac Pro
Step 2.Then select the partition which needs to reset cluster size and choose Format Partition feature from the left panel.
Step 3.On the pop-up window, you can set partition label, file system and cluster size for the selected partition. Set the file system to exFAT and choose a cluster size from the drop-down menu according to your needs and then click OK.
Step 4.Preview the changes you just made. At last, click the Apply button to allow the change.
Mac Os Exfat Support
Change Allocation Unit Size exFATwith Command Prompt
Command Prompt, is also known as CMD, is the command-line interpreter available in Windows operating system. It can help you perform a lot of operations to solve various Windows problem and manage disks and partitions.
If you are familiar with Windows 10 Command Prompt, You can also use Command Prompt to format your partition and change its allocation unit size with commands. Just follow the steps below.
Step 1: Type cmd in the Windows 10 Cortana search box and right click the best match Command Prompt to select Run as administrator.
Step 2: In the Command Prompt window, type diskpart and hit Enter.
Step 3: then type the following commands one by one and hit Enter after each:
- List disk
- Select disk * (* refers to the number of the target disk or partition)
- List partition
- Select partition *
- Format fs=exFAT unit=32k (you can just change the 32k to other allocation unit sizes you want.)
After the above commands are executed successfully, you can store files to the exFAT partition with the new allocation unit size.
You may be interested in this post: 10 Command Prompt Tricks that Every Windows User Should Know
Bottom Line
After reading this post, now you should know what allocation unit size you should use for exFAT partition and how to change exFAT allocation unit size or cluster size with two different methods.
If you have any good idea on allocation unit size for exFAT format or if you have any question about how to change cluster size exFAT with MiniTool Partition Wizard Free Edition, you can leave a message on the following comment zone and we will reply as soon as possible. If you need any help when using MiniTool software, you can contact us via [email protected].
Allocation Unit Size exFAT FAQ
Whether you’re formatting an internal drive, external drive, USB flash drive, or SD card, Windows will give you the choice of NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT. The Format dialog in Windows doesn’t explain the difference, so we will.
FAT32 is an older file system that’s largely relegated to USB flash drives and other external drives. Windows uses NTFS for its system drive, and it’s also ideal for other internal drives. exFAT is a modern replacement for FAT32, and more devices support it than do NTFS — although it’s not as widespread as FAT32.
FAT32
This file system’s age has advantages and disadvantages. Because it’s so old, it’s the de-facto standard. Flash drives you purchase will often come formatted with FAT32 for maximum compatibility across not just modern computers, but other devices like game consoles and anything with a USB port.
Limitations come with that age, however. Individual files on a FAT32 drive can’t be over 4 GB in size — that’s the maximum. A FAT32 partition must also be less than 8 TB, which is less of a limitations — but still a noticeable one if you have a new, high-capacity mechanical drive.
While this file system is okay for USB flash drives and other external media, you won’t want to use this for an internal drive. It lacks the permissions and other security features built into the more modern NTFS file system. Modern versions of Windows can no longer be installed to FAT32, and must be installed onto drives formatted with NTFS.
Compatibility: Works with all versions of Windows, Mac, Linux, game consoles, and practically anything with a USB port.
Limits: 4 GB maximum file size, 8 TB maximum partition size.
Ideal Use: Use it on removable drives for maximum compatibility with the widest range of devices, assuming you don’t have any files 4 GB or larger in size.
NTFS
Exfat For Mac
NTFS is the modern file system Windows likes to use. When you install Windows, it formats your system drive with the NTFS file system. NTFS has file size and partition size limits that are so theoretically huge you won’t run up against them. NTFS first appeared in consumer versions of Windows with Windows XP.
Aside from these limitations, NTFS is packed with other modern features. It supports file permissions for security, a change journal that can help quickly recover errors if your computer crashes, shadow copies for backups, encryption, disk quota limits, hard links, and other various features. Many of these are crucial for an operating system drive — especially file permissions.
Your Windows system partition must be NTFS. If you have a secondary drive alongside Windows and you plan on installing programs to it, you should probably go ahead and make it NTFS, too.
However, NTFS just isn’t as compatible with other operating systems. It’ll work with all recent versions of Windows — all the way back to Windows XP — but it has limited compatibility with other operating systems. By default, Mac OS X can only read NTFS drives, not write to them. Some Linux distributions may enable NTFS-writing support, but some may be read-only. None of Sony’s PlayStation consoles support NTFS. Even Microsoft’s own Xbox 360 can’t read NTFS drives, although the new Xbox One can. Other devices are even less likely to support NTFS.
Compatibility: Works with all versions of Windows, but read-only with Mac by default, and may be read-only by default with some Linux distributions. Other devices — with the exception of Microsoft’s Xbox One — probably won’t support NTFS.
Limits: No realistic file-size or partition size limits.
Ideal Use: Use it for your Windows system drive and other internal drives that will just be used with Windows.
exFAT
Ian alex mac the homecoming. It’s a file system optimized for flash drives. It’s designed to be a lightweight file system like FAT32 without all NTFS’s extra features and overhead, but without FAT32’s limitations.
Like NTFS, exFAT has very large file size and partition size limits. This means you can store files that are larger than 4 GB apiece on a flash drive or SD card if it’s formatted with exFAT. exFAT is a strict upgrade over FAT32, and should be the best choice for external drives where you want a lightweight file system without FAT32’s file size limits.
exFAT is also more compatible than NTFS. While Mac OS X includes only read-only support for NTFS, Macs offer full read-write support for exFAT. exFAT drives can be accessed on Linux by installing the appropriate software.
While exFAT is compatible with Macs — and will be compatible with some devices that don’t support NTFS, like digital cameras — it still isn’t quite as compatible. Microsoft’s own Xbox 360 doesn’t support it, although the Xbox One does. The PlayStation 3 doesn’t support exFAT drives, although the PlayStation 4 reportedly does. Various other older devices may only support FAT32 instead of exFAT.
Compatibility: Works with all versions of Windows and modern versions of Mac OS X, but requires additional software on Linux. More devices support exFAT than support NTFS, but some — particularly older ones — may only support FAT32.
Limits: No realistic file-size or partition-size limits.
Ideal Use: Use it for USB flash drives and other external drives, especially if you need files of over 4 GB in size. Assuming every device you want to use the drive with supports exFAT, you should format your device with exFAT instead of FAT32.
NTFS is ideal for internal drives, while exFAT is generally ideal for flash drives. However, you may sometimes need to format an external drive with FAT32 if exFAT isn’t supported on a device you need to use it with.
CREDIT: HOWTOGEEK.COM

Exfat Support Mac
UNDER MAINTENANCE